1372. Longest ZigZag Path in a Binary Tree
1. Description
You are given the root of a binary tree.
A ZigZag path for a binary tree is defined as follow:
- Choose any node in the binary tree and a direction (right or left).
- If the current direction is right, move to the right child of the current node; otherwise, move to the left child.
- Change the direction from right to left or from left to right.
- Repeat the second and third steps until you can’t move in the tree.
Zigzag length is defined as the number of nodes visited - 1. (A single node has a length of 0).
Return the longest ZigZag path contained in that tree.
2. Example
Example 1
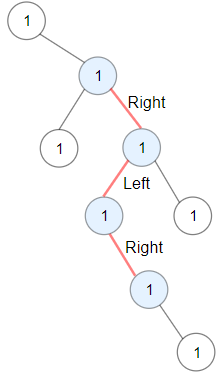
Input: root = [1,null,1,1,1,null,null,1,1,null,1,null,null,null,1]
Output: 3
Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (right -> left -> right).
Example 2
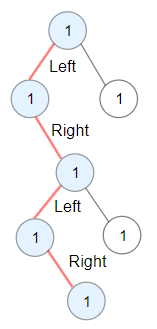
Input: root = [1,1,1,null,1,null,null,1,1,null,1]
Output: 4
Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (left -> right -> left -> right).
Example 3
Input: root = [1]
Output: 0
3. Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 5 * $10^4$].
- 1 <= Node.val <= 100
4. Solutions
Depth-First Search
n is the number of nodes in root
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
class Solution {
public:
int longestZigZag(TreeNode *root) {
int longest_path = 0;
search_longest_zigzag(root->left, 0, 1, longest_path);
search_longest_zigzag(root->right, 0, 1, longest_path);
return longest_path;
}
private:
void search_longest_zigzag(TreeNode *root, int direction, int length, int &longest_path) {
if (root != nullptr) {
longest_path = max(length, longest_path);
search_longest_zigzag(root->left, 0, direction == 1 ? length + 1 : 1, longest_path);
search_longest_zigzag(root->right, 1, direction == 0 ? length + 1 : 1, longest_path);
}
}
};