437. Path Sum III
1. Description
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return the number of paths where the sum of the values along the path equals targetSum.
The path does not need to start or end at the root or a leaf, but it must go downwards (i.e., traveling only from parent nodes to child nodes).
2. Example
Example 1
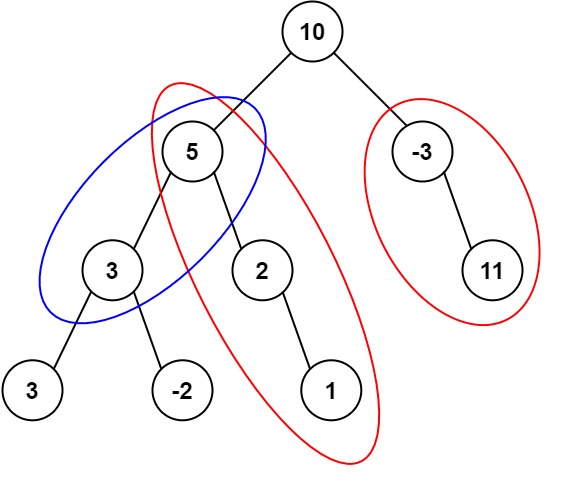
Input: root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], targetSum = 8
Output: 3
Explanation: The paths that sum to 8 are shown.
Example 2
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
Output: 3
3. Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 1000].
- -$10^9$ <= Node.val <= $10^9$
- -1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
4. Solutions
Prefix Sum
n is the number of nodes root
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
class Solution {
public:
int pathSum(TreeNode *root, int targetSum) {
int possible_cases = 0;
// Note: the initial pair {0, 1} is required.
// It represents an empty prefix sum before the root.
// For example, when target_sum == 5 and root->val == 5,
// current_sum - target_sum == 0, and this allows the path
// starting from the root to be counted correctly.
unordered_map<long long, int> path_sum_count{{0, 1}};
count_path_sum(root, targetSum, 0, possible_cases, path_sum_count);
return possible_cases;
}
private:
void count_path_sum(
TreeNode *root,
int target_sum,
long long current_sum,
int &possible_cases,
unordered_map<long long, int> &path_sum_count) {
if (root != nullptr) {
current_sum += root->val;
// The path does not have to start from the root.
// Let prefix_sum be the sum before the current node, and total_sum be the sum up to the
// current node. If total_sum - prefix_sum == target_sum, then the path between them
// forms a valid answer. Therefore, we count how many times (total_sum - target_sum) has
// appeared as a prefix sum.
possible_cases += path_sum_count[current_sum - target_sum];
++path_sum_count[current_sum];
count_path_sum(root->left, target_sum, current_sum, possible_cases, path_sum_count);
count_path_sum(root->right, target_sum, current_sum, possible_cases, path_sum_count);
--path_sum_count[current_sum];
}
}
};