687. Longest Univalue Path
1. Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return the length of the longest path, where each node in the path has the same value. This path may or may not pass through the root.
The length of the path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
2. Example
Example 1:
Input: root = [5,4,5,1,1,5]
Output: 2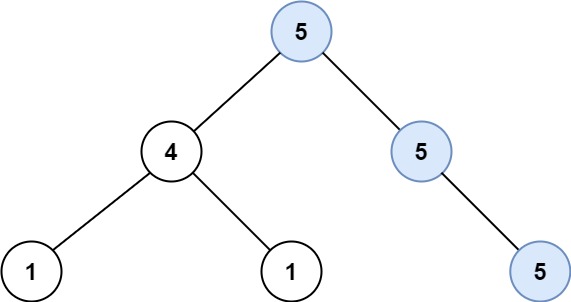
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,4,5,4,4,5]
Output: 2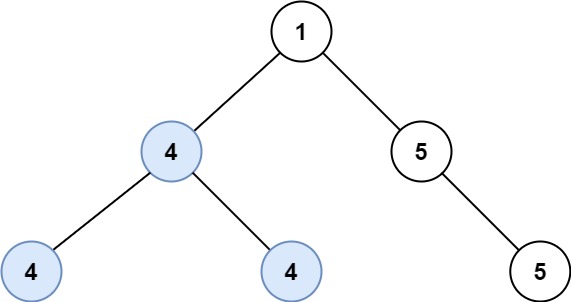
3. Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, $10^4$].
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
- The depth of the tree will not exceed 1000.
4. Solutions
My Accepted Solution
n is the number of nodes in i_root
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
class Solution
{
private:
int result = 0;
int getLongesPathLength(TreeNode *i_root)
{
if(!i_root) return 0;
int leftChildLongestPath = getLongesPathLength(i_root->left);
int rightChildLongestPath = getLongesPathLength(i_root->right);
int pathToLeftChildLength = 0, pathToRightChildLength = 0;
if(i_root->left && i_root->left->val == i_root->val)
pathToLeftChildLength = leftChildLongestPath + 1;
if(i_root->right && i_root->right->val == i_root->val)
pathToRightChildLength = rightChildLongestPath + 1;
result = max(result, pathToLeftChildLength + pathToRightChildLength);
return max(pathToLeftChildLength, pathToRightChildLength);
}
public:
// int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode* root)
int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode *i_root)
{
getLongesPathLength(i_root);
return result;
}
};