861. Score After Flipping Matrix
1. Description
You are given an m x n binary matrix grid.
A move consists of choosing any row or column and toggling each value in that row or column (i.e., changing all 0’s to 1’s, and all 1’s to 0’s).
Every row of the matrix is interpreted as a binary number, and the score of the matrix is the sum of these numbers.
Return the highest possible score after making any number of moves (including zero moves).
2. Example
Example 1
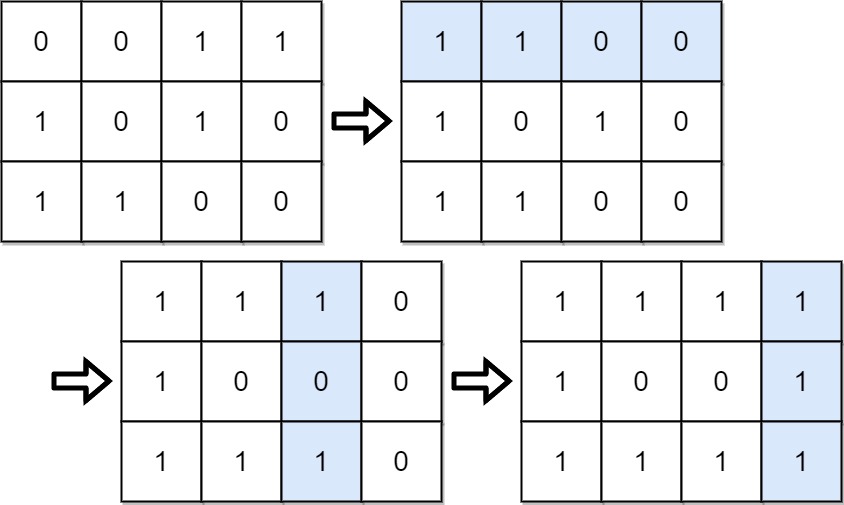
Input: grid = [[0,0,1,1],[1,0,1,0],[1,1,0,0]]
Output: 39
Explanation: 0b1111 + 0b1001 + 0b1111 = 15 + 9 + 15 = 39
Example 2
Input: grid = [[0]]
Output: 1
3. Constraints
- m == grid.length
- n == grid[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 20
- grid[i][j] is either 0 or 1.
4. Solutions
Greedy
m = grid.size(), n = grid.front().size()
Time complexity: O(mn)
Space complexity: O(1)
// To maximize the total score, make sure the first column (MSB) is all 1s:
// if a row starts with 0, flip that row (this always increases the score).
// For each remaining column, choose whether to flip the column so that it contains more 1s than 0s.
// We don't need to actually perform/record row flips: whether a row is flipped is determined by grid[row][0].
class Solution {
public:
int matrixScore(const vector<vector<int>> &grid) {
const int m = grid.size(), n = grid.front().size();
int sum = m * (1 << (n - 1));
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int one_count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
if ((grid[j][0] ^ grid[j][i]) == 1) {
++one_count;
}
}
sum += max(one_count, m - one_count) * (1 << (n - 1 - i));
}
return sum;
}
};