863. All Nodes Distance K in Binary Tree
1. Description
Given the root of a binary tree, the value of a target node target, and an integer k, return an array of the values of all nodes that have a distance k from the target node.
You can return the answer in any order.
2. Example
Example 1: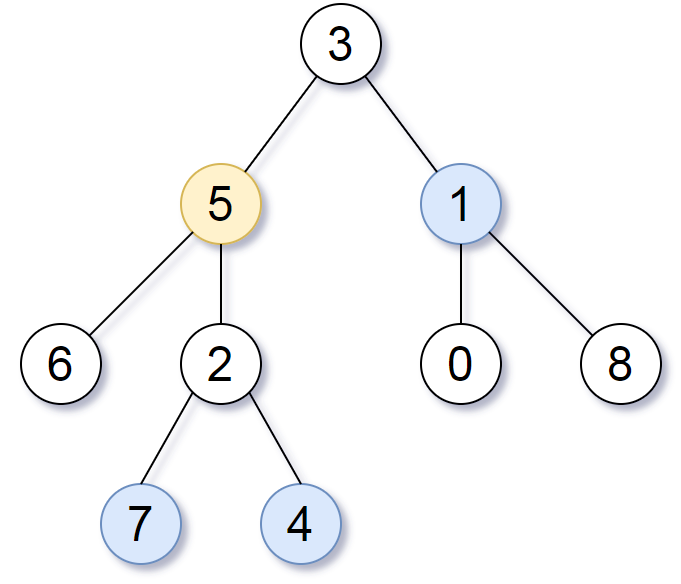
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], target = 5, k = 2
Output: [7,4,1]
Explanation: The nodes that are a distance 2 from the target node (with value 5) have values 7, 4, and 1.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1], target = 1, k = 3
Output: []
3. Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 500].
- 0 <= Node.val <= 500
- All the values Node.val are unique.
- target is the value of one of the nodes in the tree.
- 0 <= k <= 1000
4. Solutions
Hash Table & Breadth-First Search
n is the number of nodes in root
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> distanceK(TreeNode *root, TreeNode *target, int k) {
mark_parent(root, nullptr);
find_results(target, k);
return result;
}
private:
map<TreeNode *, TreeNode *> parent;
map<TreeNode *, int> is_node_on_path;
vector<int> result;
void mark_parent(TreeNode *root, TreeNode *par) {
if (root != nullptr) {
parent[root] = par;
mark_parent(root->left, root);
mark_parent(root->right, root);
}
}
void find_results(TreeNode *root, int k) {
if (root != nullptr && is_node_on_path[root] == 0) {
if (k == 0) {
result.push_back(root->val);
} else {
is_node_on_path[root] = 1;
find_results(root->left, k - 1);
find_results(root->right, k - 1);
find_results(parent[root], k - 1);
}
}
}
};