865. Smallest Subtree with all the Deepest Nodes
1. Description
Given the root of a binary tree, the depth of each node is the shortest distance to the root.
Return the smallest subtree such that it contains all the deepest nodes in the original tree.
A node is called the deepest if it has the largest depth possible among any node in the entire tree.
The subtree of a node is a tree consisting of that node, plus the set of all descendants of that node.
2. Example
Example 1: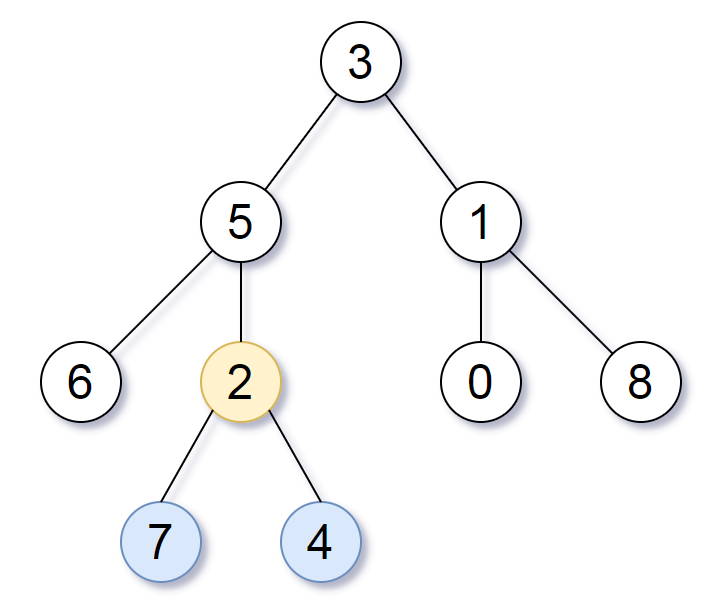
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
Output: [2,7,4]
Explanation: We return the node with value 2, colored in yellow in the diagram.
The nodes coloured in blue are the deepest nodes of the tree.
Notice that nodes 5, 3 and 2 contain the deepest nodes in the tree but node 2 is the smallest subtree among them, so we return it.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Explanation: The root is the deepest node in the tree.
Example 3:
Input: root = [0,1,3,null,2]
Output: [2]
Explanation: The deepest node in the tree is 2, the valid subtrees are the subtrees of nodes 2, 1 and 0 but the subtree of node 2 is the smallest.
3. Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range [1, 500].
- 0 <= Node.val <= 500
- The values of the nodes in the tree are unique.
4. Solutions
Depth-First Search
n is the number of nodes in root
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode *subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode *root) {
get_max_depth_(root, 0);
return result_ == nullptr ? root : result_;
}
private:
int max_depth_ = 0;
TreeNode *result_ = nullptr;
int get_max_depth_(TreeNode *root, int depth) {
if (root == nullptr) {
// null should return depth rathen than 0
return depth;
} else {
int current_depth = depth + 1;
max_depth_ = max(current_depth, max_depth_);
int left_max_depth = get_max_depth_(root->left, current_depth);
int right_max_depth = get_max_depth_(root->right, current_depth);
if (left_max_depth == max_depth_ && right_max_depth == max_depth_) {
// if only one child's max depth is the max depth, then the answer is that child
// all required nodes should have the same depth, i.e., max depth
result_ = root;
}
return max(left_max_depth, right_max_depth);
}
}
};