872. Leaf-Similar Trees
1. Description
Consider all the leaves of a binary tree, from left to right order, the values of those leaves form a leaf value sequence.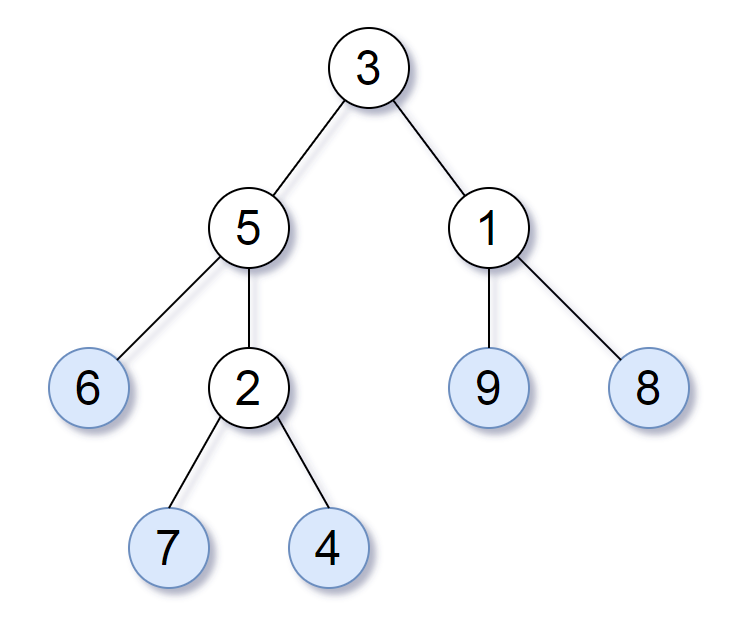
For example, in the given tree above, the leaf value sequence is (6, 7, 4, 9, 8).
Two binary trees are considered leaf-similar if their leaf value sequence is the same.
Return true if and only if the two given trees with head nodes root1 and root2 are leaf-similar.
2. Example
Example 1
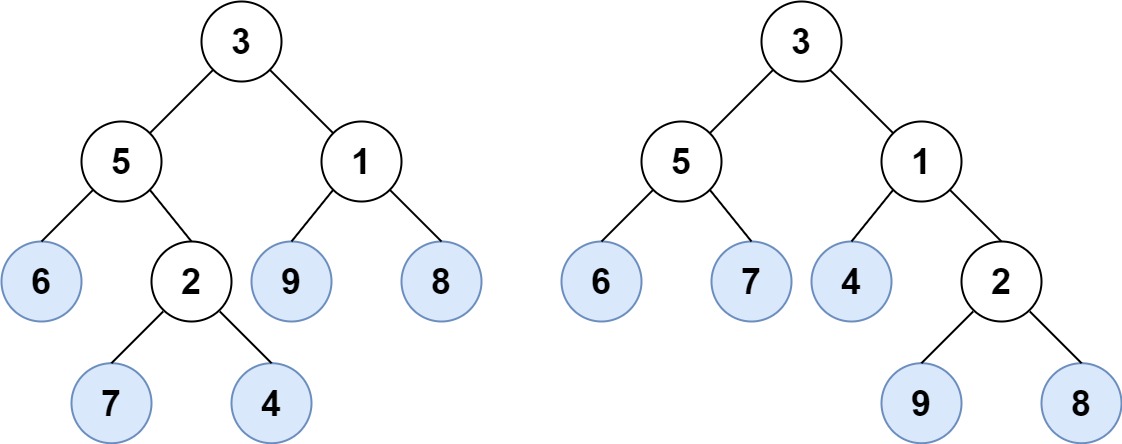
Input: root1 = [3,5,1,6,2,9,8,null,null,7,4], root2 = [3,5,1,6,7,4,2,null,null,null,null,null,null,9,8]
Output: true
Example 2
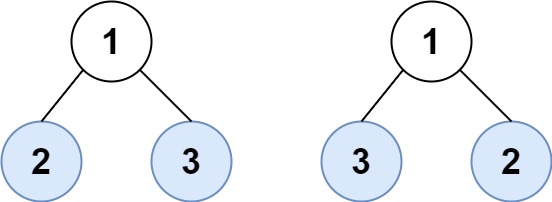
Input: root1 = [1,2,3], root2 = [1,3,2]
Output: false
3. Constraints
- The number of nodes in each tree will be in the range [1, 200].
- Both of the given trees will have values in the range [0, 200].
4. Solutions
Depth-First Search
m is the number of nodes in root1, n is the number of nodes in root2
Time complexity: O(m + n)
Space complexity: O(m + n)
class Solution {
public:
bool leafSimilar(TreeNode *root1, TreeNode *root2) {
vector<int> leaf_nodes1, leaf_nodes2;
save_leaf_nodes(root1, leaf_nodes1);
save_leaf_nodes(root2, leaf_nodes2);
return leaf_nodes1 == leaf_nodes2;
}
private:
void save_leaf_nodes(TreeNode *root, vector<int> &leaf_nodes) {
if (root != nullptr) {
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {
leaf_nodes.push_back(root->val);
}
save_leaf_nodes(root->left, leaf_nodes);
save_leaf_nodes(root->right, leaf_nodes);
}
}
};