931. Minimum Falling Path Sum
1. Description
Given an n x n array of integers matrix, return the minimum sum of any falling path through matrix.
A falling path starts at any element in the first row and chooses the element in the next row that is either directly below or diagonally left/right. Specifically, the next element from position (row, col) will be (row + 1, col - 1), (row + 1, col), or (row + 1, col + 1).
2. Example
Example 1: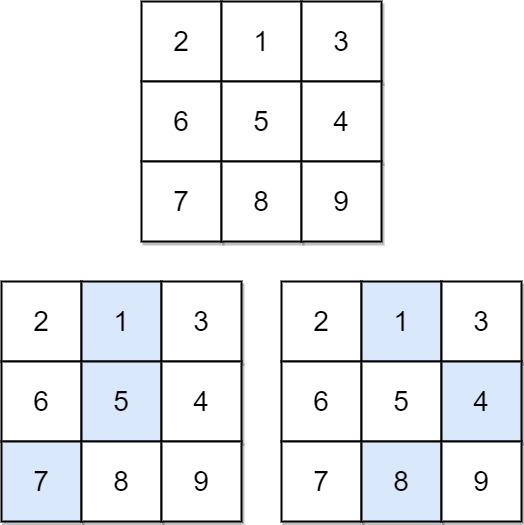
Input: matrix = [[2,1,3],[6,5,4],[7,8,9]]
Output: 13
Explanation: There are two falling paths with a minimum sum as shown.
Example 2: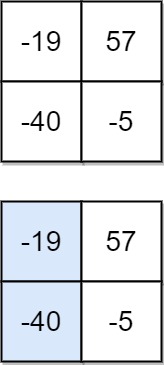
Input: matrix = [[-19,57],[-40,-5]]
Output: -59
Explanation: The falling path with a minimum sum is shown.
3. Constraints
- n == matrix.length == matrix[i].length
- 1 <= n <= 100
- -100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100
4. Solutions
Dynamic Programming
n = matrix.size()
Time complexity: O($n^2$)
Space complexity: O(n)
// we don't change the original matrix even it will help us save some memory
class Solution {
public:
int minFallingPathSum(const vector<vector<int>> &matrix) {
vector<int> falling_sum(matrix.size() + 2);
falling_sum.front() = falling_sum.back() = 10000; // 100(max rows) * 100(max value)
for (int row = 0; row < matrix.size(); ++row) {
int last_row_falling_sum = 10000; // we need the last row's value, but we will update it
for (int i = 1; i <= matrix.size(); ++i) {
int temp = falling_sum[i];
falling_sum[i] = matrix[row][i - 1] +
min({last_row_falling_sum, falling_sum[i], falling_sum[i + 1]});
last_row_falling_sum = temp;
}
}
return *min_element(falling_sum.begin(), falling_sum.end());
}
};