117. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
1. Description
Given a binary tree
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
2. Example
Example 1: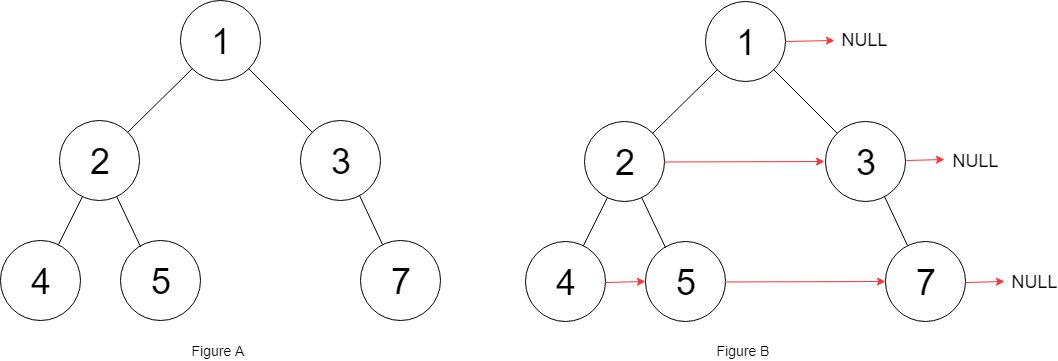
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#]
Explanation: Given the above binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B. The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers, with ‘#’ signifying the end of each level.
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
3. Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 6000].
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
4. Follow Up
- You may only use constant extra space.
- The recursive approach is fine. You may assume implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
5. Solutions
Breadth-First Search & Queue
n is the number of nodes in the tree
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
class Solution {
public:
Node *connect(Node *root) {
queue<Node *> nodes{{root}};
while (!nodes.empty()) {
int level_size = nodes.size();
auto first_node = nodes.front();
nodes.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < level_size; ++i) {
if (i > 0) {
auto second_node = nodes.front();
nodes.pop();
first_node->next = second_node;
first_node = second_node;
}
if (first_node->left != nullptr) {
nodes.push(first_node->left);
}
if (first_node->right != nullptr) {
nodes.push(first_node->right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
};
Breadth-First Search & Fake Linked List
n is the number of nodes in the tree
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
Node *connect(Node *root) {
auto iter = root;
Node *head = new Node();
while (iter != nullptr) {
auto prev = head;
while (iter != nullptr) {
if (iter->left != nullptr) {
prev->next = iter->left; // update head(only one time)
prev = prev->next;
}
if (iter->right != nullptr) {
prev->next = iter->right; // update head(only one time)
prev = prev->next;
}
iter = iter->next;
}
iter = head->next;
head->next = nullptr;
}
return root;
}
};